Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- Agent-Based Monitoring
- Data Providers
- Directory Services
- Auditing
- Hosts
- Templates
- Template Properties
- Batch Update Templates
- Log Management Templates
- File and Directory Monitor Templates
- Windows Monitor Templates
- Account Lockout Monitor Template
- Logon Monitor Template
- CPU Monitor Template
- Memory Monitor Template
- Disk Space Monitor Template
- SMART Monitor Template
- Windows Update Template
- Process Monitor Template
- Service Monitor Template
- Performance Counter Monitor Template
- PowerShell Template
- Registry Value Monitor Template
- Active Directory User Monitor Template
- Active Directory User Integrity Monitor Template
- Task Scheduler Template
- Clock Synchronization Template
- Defragment NTFS Disks Template
- Network and Application Monitor Templates
- Database Monitor Template
- Directory Service Monitor Template
- DNS Blacklist Monitor Template
- DNS Monitor Template
- Domain Expiration Monitor Template
- Network Speed Monitor Template
- Ping Monitor Template
- Database Table Reseed
- SQL Server Shrink and Backup Template
- SSH Shell
- TCP Port Scan Monitor Template
- Website Monitor Template
- SSL Certificate Monitor Templates
- Email Monitor Templates
- SNMP Monitor Templates
- Monitors
- Reports
- Auto-Configurators
- Filters
- Actions
- Desktop Actions
- Email Actions
- Event Log Actions
- Executable Actions
- File Actions
- IIS IP Address Restriction Actions
- Microsoft Teams Actions
- PowerShell Actions
- Report Actions
- Service Actions
- SMS Actions
- SNMP Trap Actions
- Syslog Actions
- Template Actions
- IIS IP Address Restriction Actions
- Action Variables
- Schedules
- Environment Variables
- Options
- Account Lockout Monitoring and Reporting
- Merging Logs
- SNMP
- SSH Shell
- Syslog
- Exporting and Importing Configuration Objects
- Shared Views
- Auto-Config Host Assignment Properties
- General Executable Properties
- Assign Actions
- Assign Directories
- Assign Disks
- Assign Shares
- Assign Files
- Assign Consolidated Logs
- Assign Event Logs
- Assign Azure Audit Logs
- Target Files and Sub-Directories
- Define Log Entry Columns
- Define Log Entry Columns with Regular Expressions
- Define CSV and W3C Log Entry Columns
- Active Directory User and Group Filters
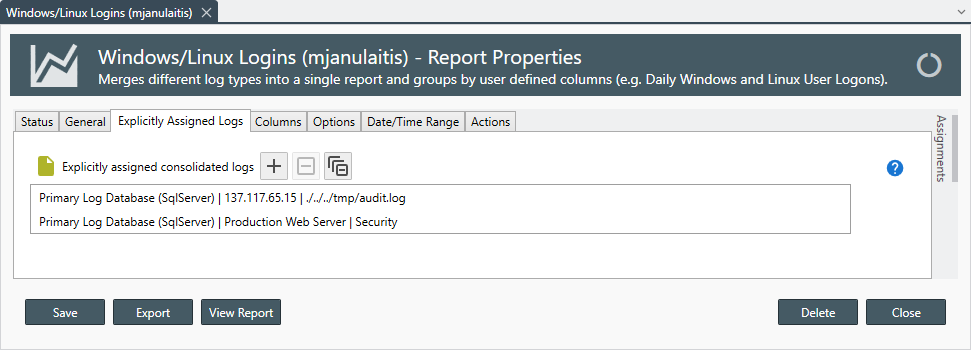
- Explicitly Assigned Logs
- File Explorer
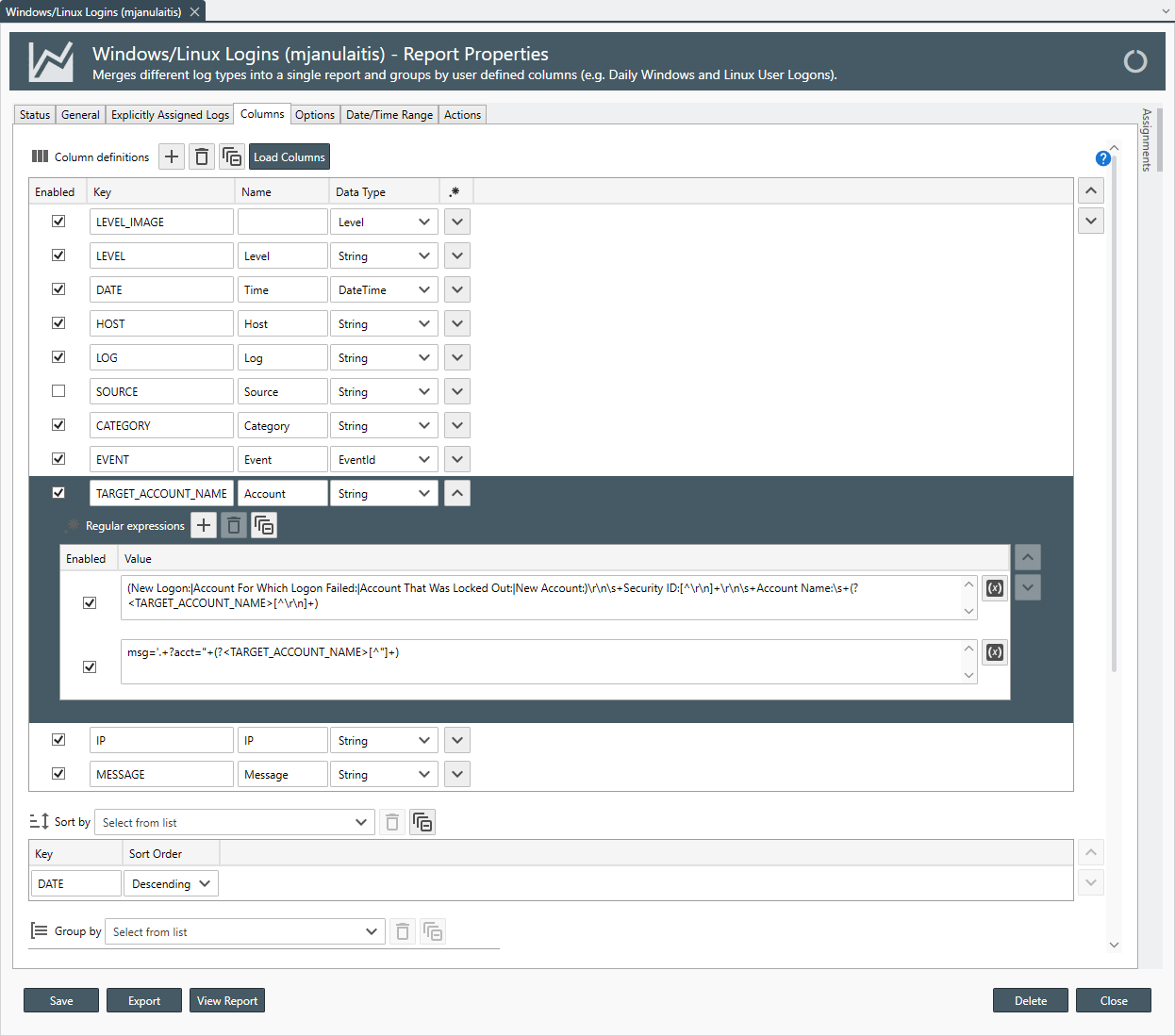
- Report Columns
- Report Date/Time Ranges
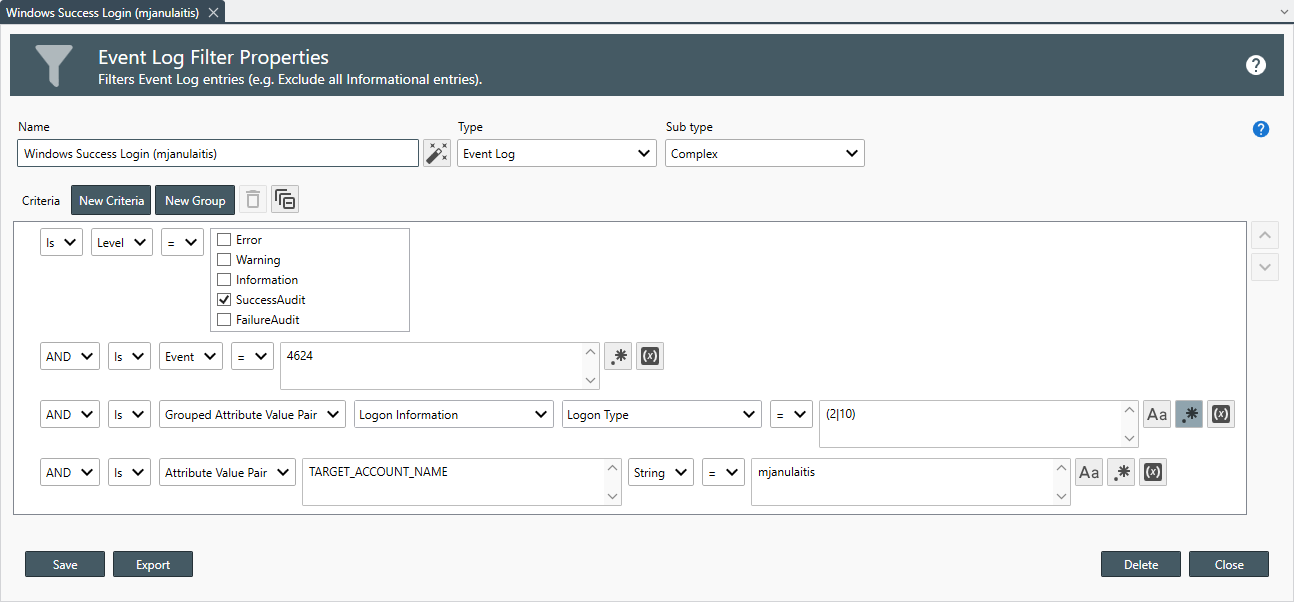
- Report Security Event Log Filters
- Select Folder or File
- Executable Timeline
- Command Line Interface
- Troubleshooting
- Terminology
SIEM Reports
A SIEM Report queiries centralized log databases for specific log entries generated from various log types on multiple servers, workstations and network devices, applies log entry filters, applies display options, such as the column order, group by and sort by rules, then lastly, displays, saves or emails the output results.
This report is typically used by network administrators that want to analyze and correlate Security Event Logs and data from various sources within their organization's network infrastructure, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and servers.
 |
To quickly view logs of the same type, see: Merging Logs. |
SIEM Reports optionally use Regular Expressions to parse log entries, extract values, validate subject and target accounts in Active Directory (when applicable), then, finally, filter entries using each assigned log type's native filters.
How to create a SIEM Report
- From the Menu Bar select File | New. The Create New Object View displays.
- From the Create New Object View, expand Reports.
-
Expand Report | Log Consolidation Reports then select SIEM Report. The Properties View displays.

Unlicensed report types appear in gray text. If you would like to create a report that is not currently licensed, please contact Corner Bowl Software to upgrade your license. -
The Properties View contains 6 configuration tabs.
- General
- Explicitly Assigned Logs
-
Columns

If you apply regular expressions column definitions in your corresponding log consolidation templates, and the column keys are identical between log types, you do not need to re-apply the regular expressions in the report. - Options
- Date/Time Range
- Actions
The Options Tab
-
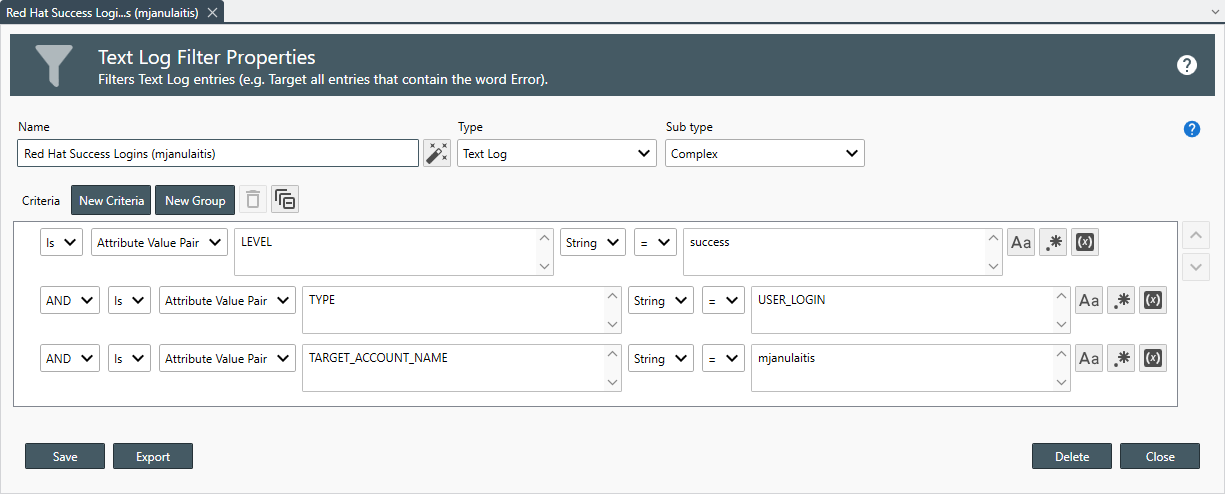
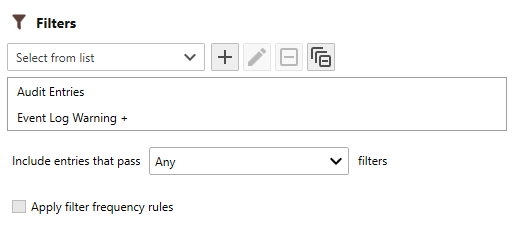
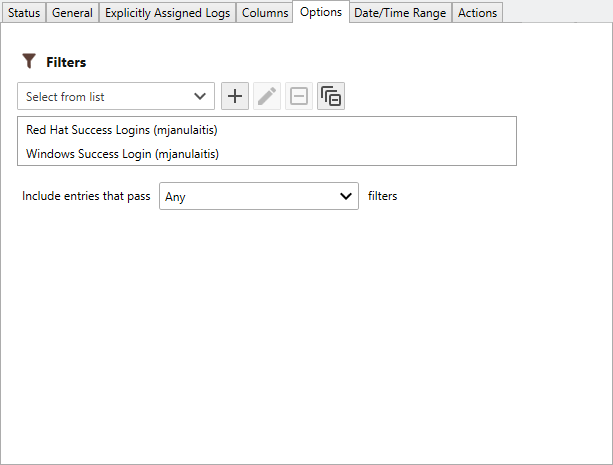
Use the Filters drop-down to select all of the filters you would like to apply to the report.
Filters are only applied to corresponding log entries types. For example, when you have assigned both an Event Log and a Text Log to the report, Event Log Filters are only applied to Event Log Entries while Text Log Filters are only applied to Text Log Entries. -
Once a filter is assigned, use the Include entries that pass drop-down to select the filter method.
The following filter options are available:
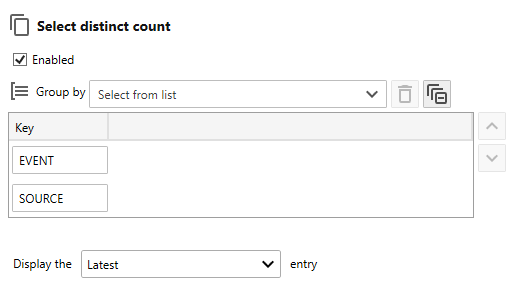
Option Description All Include each entry that passes all assigned filters of the same type. Any Include each entry that passes any filter of the same type. None Include each entry that does not pass any of the filters of the same type. Ignore Include all entries. - Use the Select distinct count controls to define a composite key to select a distinct count of entries that match your composite key. For example, generate a report that displays the number of each unique event type, Information, Warning, Critical, Audit Success and Audit Failure or the number of unique entries keyed by Event ID and Source on each assigned host).
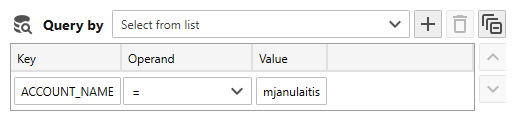
- Use the Query by controls to optimize SQL statements. For example, if the column you want to search for was added using a regular expression column defnition, specify the column key and the value to search for. Once executed, only rows that match your search criteria are returned from the database engine.