Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- Agent-Based Monitoring
- Data Providers
- Directory Services
- Auditing
- Hosts
- Templates
- Template Properties
- Batch Update Templates
- Log Management Templates
- File and Directory Monitor Templates
- Windows Monitor Templates
- Account Lockout Monitor Template
- Logon Monitor Template
- CPU Monitor Template
- Memory Monitor Template
- Disk Space Monitor Template
- SMART Monitor Template
- Windows Update Template
- Process Monitor Template
- Service Monitor Template
- Performance Counter Monitor Template
- PowerShell Template
- Registry Value Monitor Template
- Active Directory User Monitor Template
- Active Directory User Integrity Monitor Template
- Task Scheduler Template
- Clock Synchronization Template
- Defragment NTFS Disks Template
- Network and Application Monitor Templates
- Database Monitor Template
- Directory Service Monitor Template
- DNS Blacklist Monitor Template
- DNS Monitor Template
- Domain Expiration Monitor Template
- Network Speed Monitor Template
- Ping Monitor Template
- Database Table Reseed
- SQL Server Shrink and Backup Template
- SSH Shell
- TCP Port Scan Monitor Template
- Website Monitor Template
- SSL Certificate Monitor Templates
- Email Monitor Templates
- SNMP Monitor Templates
- Monitors
- Reports
- Auto-Configurators
- Filters
- Actions
- Desktop Actions
- Email Actions
- Event Log Actions
- Executable Actions
- File Actions
- IIS IP Address Restriction Actions
- Microsoft Teams Actions
- PowerShell Actions
- Report Actions
- Service Actions
- SMS Actions
- SNMP Trap Actions
- Syslog Actions
- Template Actions
- IIS IP Address Restriction Actions
- Action Variables
- Schedules
- Environment Variables
- Options
- Account Lockout Monitoring and Reporting
- Merging Logs
- SNMP
- SSH Shell
- Syslog
- Exporting and Importing Configuration Objects
- Shared Views
- Auto-Config Host Assignment Properties
- General Executable Properties
- Assign Actions
- Assign Directories
- Assign Disks
- Assign Shares
- Assign Files
- Assign Consolidated Logs
- Assign Event Logs
- Assign Azure Audit Logs
- Target Files and Sub-Directories
- Define Log Entry Columns
- Define Log Entry Columns with Regular Expressions
- Define CSV and W3C Log Entry Columns
- Active Directory User and Group Filters
- Explicitly Assigned Logs
- File Explorer
- Report Columns
- Report Date/Time Ranges
- Report Security Event Log Filters
- Select Folder or File
- Executable Timeline
- Command Line Interface
- Troubleshooting
- Terminology
Corner Bowl Server Manager
SIEM, IPS, Server Monitoring, Uptime Monitoring and Compliance Software
SNMP Trap Server Settings
Server Manager contains an internal SNMP server. The SNMP server can be used to receive and forward traps from both computers and devices such as switches, routers, firewalls, and Unix and Linux servers. By default, when a trap is received from a device, the Server Manager automatically adds the device's IP or hostname to the Explorer view and if Trap Consolidation is enabled, the trap saved to the Primary Data Provider.
In this Topic
How to configure the SNMP Trap Server
- From the Explorer View, navigate to Options, then select SNMP Trap Server Properties. The SNMP Trap Server Properties View displays.
-
The SNMP Trap Server Properties View contains 3 tabs.
- Options
- Assignments
- Columns
SNMP Trap Server
- Check the Enabled check box to enable the SNMP Trap Server.
- Use the Port text box to specify the port. The default value is 162.
- Use the Bind address text box to specify the local address to Bind the SNMP Trap Server. The default is 0.0.0.0 which binds to all local IP addresses.
- Clicking Clear DNS Cache empties any prior DNS cached values.
Options
-
Use the Add all new hosts check box to automatically add any SNMP device to the software when a SNMP trap is received from the device for the first time.
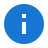
Devices sending SNMP traps to Server Manager are automatically be added to the Explorer View under the Hosts/SNMP Devices node then the templates, such as SNMP Trap Consolidation automatically assigned. If you prefer to explicitly specify which SNMP devices can save traps to the Log Database, clear this option then manually add each SNMP device you want to support. Finally, assign the SNMP Trap Consolidation template to each new SNMP device or the Host Group where you added the SNMP devices. -
Use the Host identification method drop-down to select how you would like connecting hosts to be identified.
Option Description DNS Lookup The server uses DNS to resolve the hostname. DNS and FQDN Lookup The server uses DNS and Active Directory to resolve the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). Remote IP Address The server uses the IP address.
SNMP v3
-
Use the User registry controls to manually assign each security method to enable.

To configure SNMP v3 device connectivity, see: SNMP Device Connection Properties
Object Identifier Aliases
-
Choose or create new Object Identifier Aliases with unique OIDs so Server Manager can display the friendly name in the Management Console and triggered Actions rather than the OID.

To automaitically resolve OIDs using MIB files, see: SNMP
Communities
- Choose or create new SNMP v2 Communities to listen and accept.
SNMP Device Connection Properties