Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- Agent-Based Management
- Common Tasks
- Data Providers
- Directory Services
- Auditing
- Hosts
- Templates
- Template Properties
- Batch Update Templates
- Assign Templates
- Log Management Templates
- SCAP Compliance Monitor
- Active Directory User Monitor Templates
- File and Directory Monitor Templates
- Windows Monitor Templates
- CPU Monitor Template
- Memory Monitor Template
- Disk Space Monitor Template
- Account Lockout Monitor Template
- Audit Policy Monitor Template
- Logon As Monitor Template
- Logon Monitor Template
- Performance Counter Monitor Template
- PowerShell Template
- Process Monitor Template
- RDP Session Monitor Template
- Registry Value Monitor Template
- Service Monitor Template
- SMART Disk Monitor Template
- System Security Monitor Template
- Windows Update Template
- WMI Query Template
- Task Scheduler Template
- Clock Synchronization Template
- Defragment NTFS Disks Template
- Network and Application Monitor Templates
- SSL Certificate Monitor Templates
- Database Templates
- Email Monitor Templates
- SNMP Monitor Templates
- Windows Accounts Templates
- Monitors
- Reports
- Auto-Configurators
- Filters
- Actions
- Schedules
- Environment Variables
- Options
- SNMP
- SSH Shell
- Syslog
- System Reset
- Shared Views
- Active Directory User and Group Filters
- Assign Actions
- Assign Azure Audit Logs
- Assign Consolidated Logs
- Assign Directories
- Assign Disks
- Assign Event Logs
- Assign Files
- Assign Services
- Assign Shares
- Auto-Config Host Assignment Properties
- Define CSV and W3C Log Entry Columns
- Define Log Entry Columns
- Define Log Entry Columns with Regular Expressions
- Executable Status
- Executable Timeline
- Explicitly Assigned Logs
- File Explorer
- General Executable Properties
- Report Columns
- Report Date/Time Ranges
- Report Security Event Log Filters
- Select Folder or File
- Target Files and Sub-Directories
- Command Line Interface
- Server Configuration
- Agent Configuration
- Troubleshooting
- Best Practices
- Terminology
Corner Bowl Server Manager
SIEM, IPS, Server Monitoring, Uptime Monitoring and Compliance Software
PowerShell Actions
PowerShell Actions enable you to execute specific commands and scripts in response to an event. This action is typically used as an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) by network administrators in response to Intrusion Detection System (IDS) events such as DoS and Phishing attacks.
Note
- Use this Action in conjunction with an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Template (e.g. IIS W3C Log Monitor or IIS W3C Log Consolidation configured to simultaneously monitor the file contents).
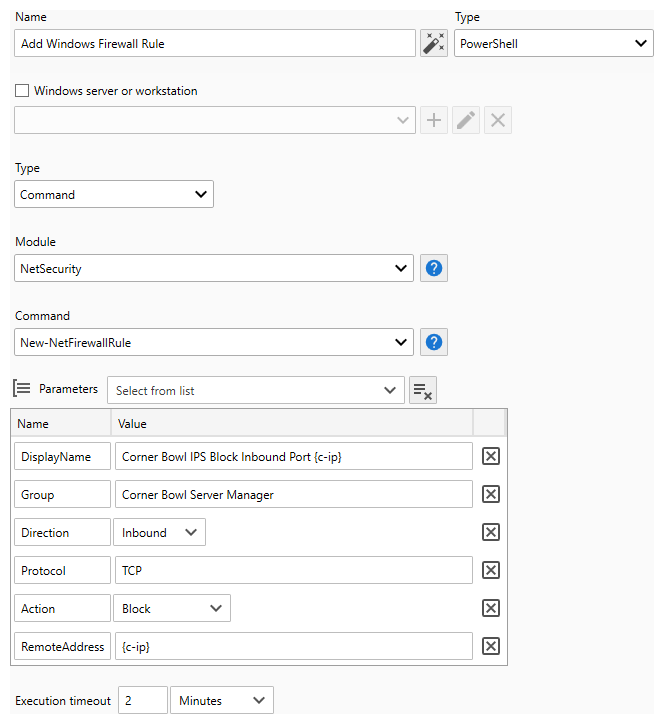
- Use the sample Add Windows Firewall Rule to automatically block DoS and Phishing attacks on your IIS or other web servers. Once the Add Windows Firewall Rule Action is assigned to the IDS Template, the result is an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) Action.
In this Topic
- How To Create a PowerShell Action
- How To Create a PowerShell Command Action
- How To Create a PowerShell Script Action
- How To Set the PowerShell Timeout
- Testing the PowerShell Action
How To Create a PowerShell Action
- From the Menu Bar select File | New. The Create New Object View displays.
- Select Alerts and Actions. The New Action view displays.
- Use the Name text box to specify a unique name.
- From the Type drop-down select PowerShell.
- Use the Windows server or workstation drop-down to target the managed server.
Important
This Action requires the Agent to be installed on each managed system and each assigned Template configured to use the Agent. For more information see: Agent-Based Management
- Use the Type drop-down to select to either run individual commands with dynamically set parameter values or run static scripts.
How To Create a PowerShell Command Action
- Use the Module drop-down to select from the list of available modules. Click the help button to view Microsoft's corresponding PowerShell documentation.
- Use the Command drop-down to select from the list of available module commands. Click the help button to view Microsoft's corresponding PowerShell documentation.
- Use the Parameters drop-down to set the command's parameter values.
Note
Use variable placeholders, keys wrapped with curly brackets {KEY}, to replace with extracted values.
For example: {c-ip} or {TARGET_ACCOUNT_NAME}
For example: {c-ip} or {TARGET_ACCOUNT_NAME}
How To Create a PowerShell Script Action
- Use the Filename drop-down to select the local script to run.
Important
When managing a remote machine, the script is uploaded to the Agent, then, executed locally on the remote machine.
- Use the Arguments text box to specify the PowerShell command-line parameters.
For example: -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
How To Set the PowerShell Timeout
- Use the Execution timeout controls to set the maximum time to wait for PowerShell to complete before triggering a timeout error.
Testing the PowerShell Action
- Use the Select server or workstation drop-down to specify the managed system to test the action on.
- When testing a Command Type, temporarily change any variable placeholders with test values.
- Click the Test button.
Important
When managing a remote machine, the commands and scripts are uploaded to the Agent, then, executed locally through the Agent on the managed machine. If the managed machine is configured to keep the Agent connected, the test is immediate, otherwise the test is queued to execute the next time the Agent connects. If the Agent is configured to connect at a frequency greater than once a minute, the test may timeout, however, the action will still be executed the next time the Agent connects.